Week 2
VL 3 - 23.04.25
- os api’s:
- a quick exmaple: system calls in windows, reading a data.
- API’s in Windows vs Posix
- Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Processes
- Process: an active, executing program
- a programm becomes a process when the OS loads the program code to the memory => same program can be started many times => multiple processes of the same program
- Memory of a process:
- stack: function calls, return addresses, variables local to the stack
- heap: dynamically allocated memory for objects and arbitrarily large data structures.
- data: global variables, constants.
- program code.
- stack and heap grow towards each other.
- Process Control Block (PCB): the way OS managemes processes (process bookkeeping) (implemented as
structin C.) - Process management: creation, deletion, etc
fork(): creates an identical child-process.execve(): replace the memory contents of a process.waitpid(): wait for the ending of a child-process._exit(): end the process
- example: a (very) mimimal, toy shell - application of
fork() init()in Posix- process creation in windows.
- process management
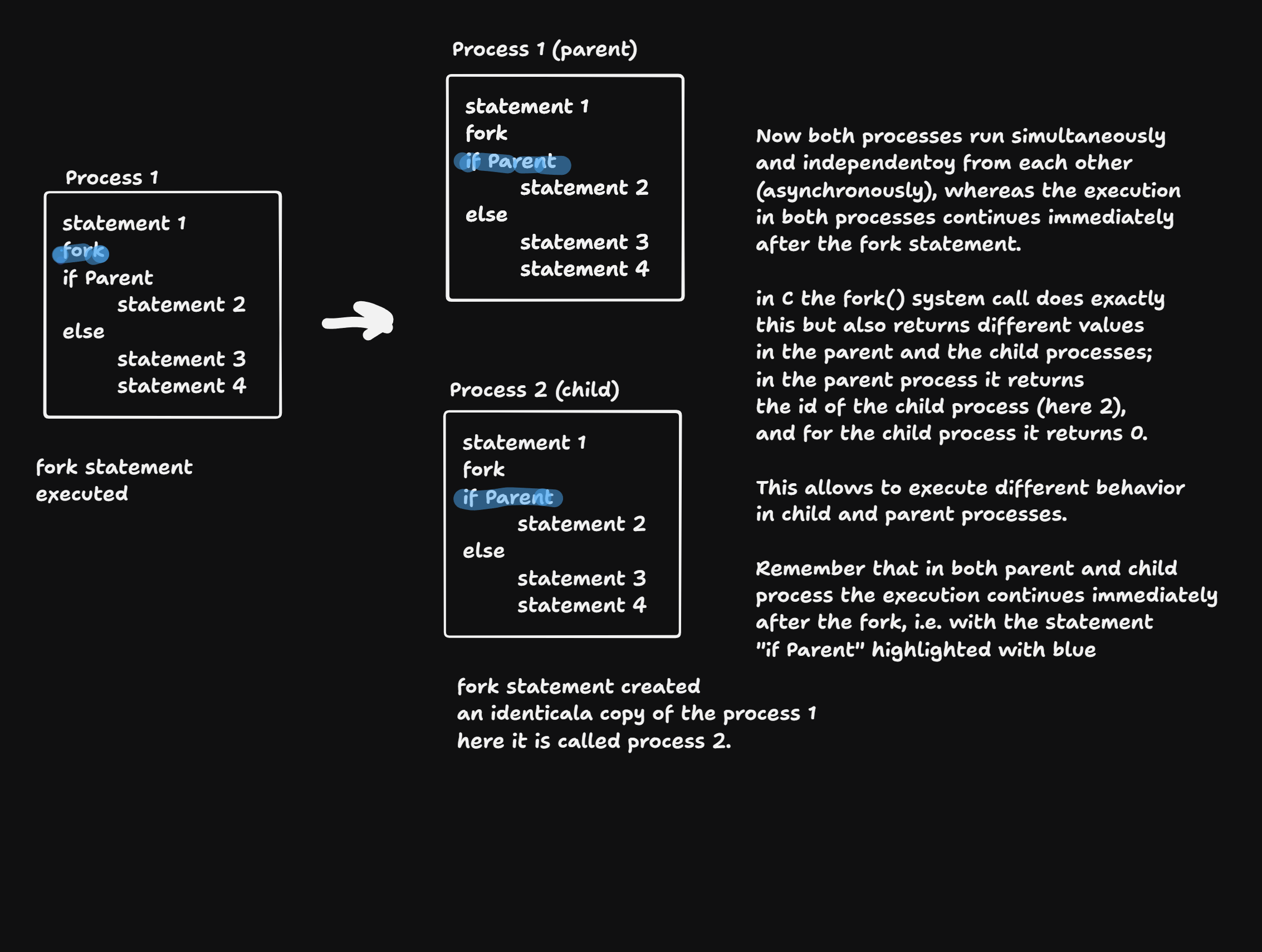
- parent and child processes can be synchonozied with a
wait()command in conjunction withfork().
## Tutorial
overview of bash
greeting="Hello, world!" echo "$greeting"